The Benefits of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses

In today’s crazy world of digital business, agility and efficiency are crucial for small businesses aiming to stay competitive. Clouds offer a transformative solution by allowing businesses to access the benefits of cloud computing resources—such as servers, storage, and applications—over the internet, eliminating the need for substantial upfront investments in physical hardware and software.
At its core, cloud computing operates on a pay-as-you-go model, where businesses only pay for the resources they use. This flexibility not only reduces costs but also enables businesses to scale their operations seamlessly as they grow. By leveraging cloud services, small businesses can access the same powerful tools and technologies that large enterprises use, fostering innovation and operational excellence without the burden of extensive IT infrastructure.
Understanding Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is a technology that allows businesses to use computing resources, like servers, storage, and applications, over the internet. Instead of buying and maintaining physical hardware, businesses can access these resources online, paying only for what they use. This approach offers many advantages, especially for small businesses.
Types of Cloud Services
Cloud services are typically categorized into various types based on their deployment models and service delivery methods. Understanding these types is essential for small businesses to select the right cloud solutions that meet their operational needs, budget constraints, and security requirements.
Cloud Deployment Models
1. Public Cloud
- Description: Public clouds are owned and operated by third-party cloud service providers (CSPs) who deliver their services over the internet. Resources such as servers and storage are shared among multiple users or organizations.
- Advantages:
- Cost-Effective: Operates on a pay-as-you-go model, eliminating the need for significant upfront investments.
- Scalability: Easily scalable to accommodate business growth or seasonal demand spikes.
- No Maintenance Responsibilities: The CSP handles all maintenance and infrastructure management.
- Examples: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP).
- Use Case for Small Businesses: A small e-commerce store using AWS to host its website can handle increased traffic during holiday seasons without investing in additional physical servers.
2. Private Cloud
- Description: A private cloud is dedicated to a single organization, offering greater control over resources and security. It can be hosted on-premises or by a third-party provider.
- Advantages:
- Enhanced Security: Provides a higher level of security and privacy, making it suitable for sensitive data.
- Compliance: Easier to comply with industry-specific regulations and standards.
- Customization: Tailored to meet specific organizational needs and workflows.
- Use Case for Small Businesses: A financial consultancy firm hosting its private cloud on-premises to ensure client data remains secure and complies with financial regulations.
3. Hybrid Cloud
- Description: This model combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to move between them as needed. It provides flexibility in resource management.
- Advantages:
- Flexibility: Businesses can maintain sensitive data in a private cloud while leveraging the scalability of the public cloud for less critical workloads.
- Cost Efficiency: Optimizes costs by balancing between on-premises infrastructure and cloud resources.
- Disaster Recovery: Enhances business continuity by enabling cloud bursting during peak demand.
- Use Case for Small Businesses: A healthcare clinic using a private cloud to store patient records while utilizing the public cloud for running administrative applications during high-demand periods.
4. Community Cloud
- Description: A community cloud is shared by several organizations with similar interests or requirements, such as compliance or security needs.
- Advantages:
- Cost-Sharing: Reduces costs by sharing infrastructure among multiple organizations.
- Tailored Security: Provides a level of privacy and security tailored to the community’s specific needs.
- Collaboration: Facilitates collaboration among organizations within the same industry or sector.
- Use Case for Small Businesses: A group of legal firms sharing a community cloud to ensure compliance with legal industry standards while benefiting from shared infrastructure costs.
Service Delivery Models
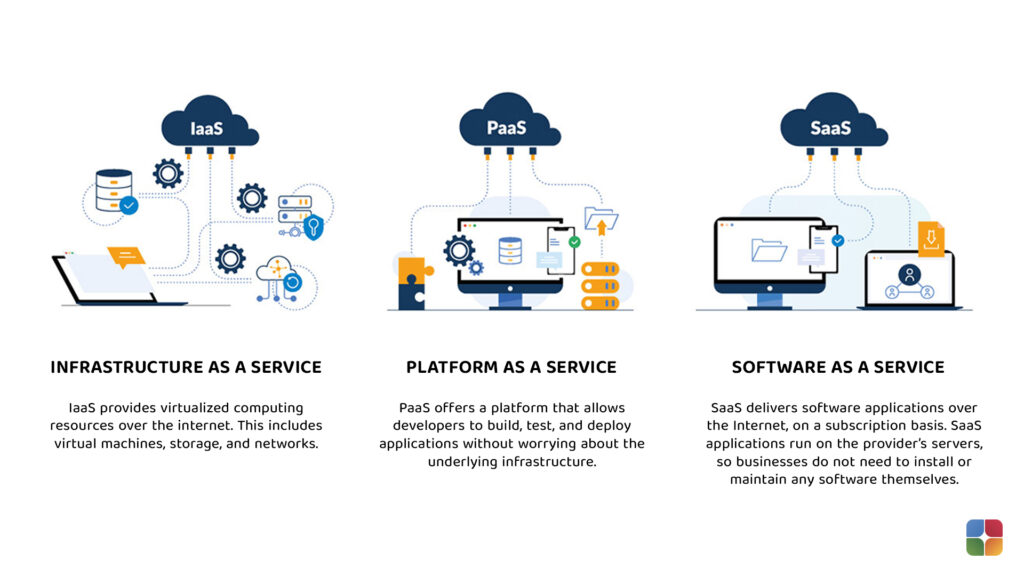
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Description: IaaS provides virtualized computing resources over the internet. Users rent IT infrastructure like servers, storage, and networking on a pay-as-you-go basis.
- Advantages:
- Scalability: Easily scale resources up or down based on business needs.
- Cost Control: Pay only for the infrastructure used, reducing capital expenditure.
- Flexibility: Allows businesses to deploy and manage applications without worrying about physical hardware.
- Use Cases for Small Businesses:
- Hosting websites and applications without investing in physical servers.
- Setting up virtual desktops for remote employees.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Description: PaaS offers a platform that allows developers to build, deploy, and manage applications without worrying about the underlying infrastructure.
- Advantages:
- Developer Efficiency: Streamlines the development process by handling infrastructure management.
- Focus on Development: Enables developers to concentrate on coding and application functionality.
- Integrated Tools: Provides integrated development tools, databases, and middleware.
- Use Cases for Small Businesses:
- Startups developing mobile or web applications using platforms like Heroku or Google App Engine.
- Small software development teams deploying applications rapidly without managing servers.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Description: SaaS delivers software applications over the internet on a subscription basis. The CSP manages everything from infrastructure to application maintenance.
- Advantages:
- Accessibility: Access applications from any device with an internet connection.
- Maintenance-Free: Eliminates the need for local installation and maintenance.
- Automatic Updates: Ensures that software is always up-to-date with the latest features and security patches.
- Use Cases for Small Businesses:
- Utilizing Google Workspace for email and document collaboration.
- Implementing Salesforce for customer relationship management (CRM).
- Adopting Microsoft 365 for productivity and collaboration tools.
4. Functions as a Service (FaaS)
- Description: FaaS allows developers to execute code in response to events without managing servers directly, focusing instead on writing individual functions.
- Advantages:
- Cost Efficiency: Pay only for the compute time consumed by functions.
- Scalability: Automatically scales with the number of requests.
- Simplified Deployment: Deploy individual functions without managing the entire application infrastructure.
- Use Cases for Small Businesses:
- Building serverless applications that automatically scale based on user demand.
- Implementing event-driven processes, such as automated backups or real-time data processing.
Popular Cloud Service Providers
Several industry-leading companies provide robust cloud computing services tailored to various business needs:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Renowned for its comprehensive suite of services, including computing power, storage solutions, and advanced databases. AWS offers specialized services like AWS Lambda for serverless computing and Amazon S3 for scalable storage.
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP): Known for its data analytics and machine learning capabilities, GCP provides tools like BigQuery for large-scale data analysis and TensorFlow for machine learning applications.
- Microsoft Azure: Offers a wide array of cloud services, including Azure Virtual Machines, Azure SQL Database, and Azure DevOps, catering to diverse business requirements from infrastructure management to application development.
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing for Small Businesses
Cloud computing presents numerous advantages that can significantly enhance the operations and growth potential of small businesses. Below, we delve deeper into each benefit, supported by real-world examples, actionable insights, and credible statistics.
1. Cost Savings

Detailed Insight: One of the most compelling advantages of cloud computing is the substantial cost savings it offers. Traditional IT infrastructure requires significant capital expenditure for purchasing hardware, software licenses, and maintenance. In contrast, cloud services operate on an Operational Expenditure (OpEx) model, allowing businesses to pay only for the resources they consume.
Success story: A small retail business transitioned from on-premises servers to AWS, resulting in a 30% reduction in IT costs. By leveraging AWS’s scalable storage solutions, the business eliminated the need for expensive hardware upgrades, instead paying for additional storage only during peak shopping seasons.
Supporting Statistics:
- Deloitte Insights reports that 93% of businesses have experienced improved financial performance through cloud services.
- IBM found that businesses using cloud computing see an average of 30% savings on IT costs.
Industry Adoption Insight: Across various industries, cloud computing is recognized as a key driver for digital transformation. 95% of respondents across industries agree or strongly agree that industry clouds present significant opportunities for accelerating digital transformation. The top anticipated benefits include 56% expecting faster innovation and time to market, and 49% anticipating accelerated organizational agility.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
Detailed Insight: Cloud computing provides unparalleled scalability, enabling businesses to adjust their resources dynamically based on demand. This flexibility is crucial for small businesses experiencing growth or seasonal fluctuations.
Example: An online retailer using Microsoft Azure can effortlessly scale their server capacity during holiday seasons to accommodate increased traffic. Post-peak, they can scale down resources, ensuring they only pay for what they use.
Industry-Specific Applications:
- Healthcare: Small clinics can scale their data storage needs as patient records grow.
- Manufacturing: Adjust computing power during production cycles to handle increased data from IoT devices.
Supporting Statistics: According to the Flexera 2024 State of the Cloud Report, 82% of enterprises and small businesses recognize scalability as a significant advantage of cloud computing.
Industry Adoption Insight: Faster innovation and accelerated change are seen as key outcomes of industry clouds across all sectors, with 56% of respondents citing faster innovation as a top benefit. This indicates that even organizations hesitant to adopt cloud solutions should prioritize these benefits to remain competitive.
3. Improved Collaboration

Detailed Insight: Cloud-based collaboration tools enhance team productivity by enabling real-time access to documents and applications from any location.
Example: A marketing agency utilizing Google Workspace allows team members to collaborate on campaigns simultaneously, regardless of their physical location. This real-time collaboration accelerates project timelines and fosters creativity.
Supporting Statistics: A study by Frost & Sullivan found that companies investing in collaboration technologies can see productivity increases of up to 400%.
Industry Adoption Insight: Across industries, the ability to innovate and respond swiftly to market changes is paramount. 49% of respondents believe that cloud computing accelerates organizational agility, further supporting the adoption of collaborative cloud tools.
4. Enhanced Security

Detailed Insight: Cloud service providers implement advanced security measures, including data encryption, regular security updates, and robust access controls, ensuring data protection beyond the capabilities of most small businesses.
Example: A financial consultancy using Salesforce benefits from built-in security features like encrypted data storage and multi-factor authentication, safeguarding sensitive client information without hefty investments in security infrastructure.
Supporting Statistics: According to a survey by Alert Logic, 66% of businesses feel more secure using cloud services compared to on-premises solutions.
Industry Adoption Insight: While security remains a top priority, 35% of respondents across industries express fear of losing control over data and insights. Addressing these concerns by highlighting the robust security measures provided by cloud services can enhance trust and adoption rates.
5. Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery
Detailed Insight: Cloud computing ensures that businesses can maintain operations and recover swiftly from disruptions through robust disaster recovery solutions.
Expanded Content: Cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer comprehensive Disaster Recovery as a Service (DRaaS), enabling businesses to replicate their data across multiple geographically dispersed data centers. For example, AWS’s Disaster Recovery Plan allows businesses to achieve low Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) and Recovery Point Objectives (RPO), ensuring minimal downtime and data loss.
Technical Metrics:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): The maximum acceptable length of time that a service can be unavailable after a disaster. AWS can achieve RTOs of minutes for critical applications.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): The maximum acceptable amount of data loss measured in time before the disaster occurs. AWS typically offers RPOs of seconds to minutes.
Success story: A small legal firm using AWS’s DRaaS recovered their critical data within minutes after a local data center outage, maintaining access to client records and ongoing cases.
Industry Adoption Insight: Across industries, 35% of respondents are concerned about protecting data in the cloud, highlighting the importance of robust disaster recovery solutions. Additionally, 33% are wary of vendor lock-in, suggesting that small businesses should consider multi-cloud strategies to mitigate these risks.
6. Access to Advanced Technologies
Detailed Insight: Cloud computing democratizes access to cutting-edge technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Big Data Analytics, enabling small businesses to innovate and compete effectively.
Example: A small e-commerce business leverages Google Cloud’s BigQuery to analyze customer purchasing patterns, enabling personalized marketing strategies that drive sales growth.
Step-by-Step Implementation Guide:
- Identify Business Needs: Assess specific challenges like customer segmentation.
- Choose the Right Tools: Select appropriate cloud-based solutions (e.g., AWS SageMaker for machine learning).
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Use APIs for seamless integration.
- Train Staff: Provide training resources to ensure effective use of new technologies.
- Monitor and Optimize: Regularly review performance metrics for continuous improvement.
Supporting Statistics: According to a report by McKinsey, companies that use AI and data analytics through cloud services can see a 20-30% increase in productivity.
Industry Adoption Insight: In the Life Sciences and Health Care (LSHC) sector, 36% of organizations prioritize creating connections with suppliers and customers, leveraging advanced cloud technologies to foster a mature digital ecosystem. However, 36% also report concerns about data protection, especially during legacy system transformations, underscoring the need for secure and compliant cloud solutions.
Industry Cloud Adoption Insights
To provide a more nuanced understanding of cloud computing’s impact, it’s essential to consider how different industries adopt and benefit from cloud services. The following insights highlight general adoption trends, specific industry benefits, and common challenges.
General Adoption
- High Agreement on Benefits: 95% of respondents across industries agree or strongly agree that industry clouds present significant opportunities for accelerating digital transformation.
- Top Benefits:
- 56%: Faster innovation and time to market.
- 49%: Accelerating organizational agility.
- 25%: Enabling more modular solution designs.
Challenges in Adoption
- Top Challenges:
- 35%: Fear of loss of control over data and insights.
- 33%: Concerns about vendor lock-in and reliance on hyperscaler solutions.
- 31%: Confidence in the ability to protect data in the cloud.
- Less Critical Challenges:
- 18%: Doubts about the success of industry clouds in highly specialized industries.
- 18%: Too few use cases to estimate the value.
Industry-Specific Insights
1. Consumer Products:
- Optimism: 46% believe industry clouds will facilitate the migration of legacy solutions.
- Key Challenge: 42% cite cost as a prohibitive factor.
- Integration: 25% report minimal concerns about integration difficulties, indicating confidence in cloud implementation with minimal customization.
2. Energy, Resources & Industrials (ER&I):
- Focus: Operational improvements and managing organizational impacts.
- Challenges:
- 29% concerned about vendor competition.
- 35% prioritize protecting data in the cloud.
3. Financial Services (FSI):
- Emphasis: 43% stress the importance of business process blueprints and meeting regulatory demands.
- Cost Concern: Only 16% find cloud adoption cost-prohibitive.
- Top Concern: 41% worry about control over data and insights.
4. Life Sciences and Health Care (LSHC):
- Priorities: 36% focus on creating connections with suppliers and customers.
- Concerns: 36% are concerned about data protection during legacy system transformations.
5. Technology, Media, and Telecommunications (TMT):
- Role: As product and platform providers, less emphasis on creating new business process blueprints.
- Challenges:
- 28% concerned about costs.
- 23% fear industry cloud success due to specialization.
Actionable Insights
1. Sector-Specific Focus:
- Consumer-Focused Industries: Should broaden their assessment of ROI from cloud adoption to justify expenses and avoid over-focusing on operational efficiencies.
- FSI and ER&I Organizations: Should address data protection concerns and consider open architecture designs to safeguard against vendor lock-in.
2. Mitigating Challenges:
- Vendor Lock-In Concerns: Exploring multi-cloud strategies can reduce dependency on single vendors.
- Security and Compliance: Cloud providers need to emphasize their ability to ensure data security and regulatory compliance, especially within highly regulated sectors like financial services and life sciences.
3. Cross-Industry Observations:
- Innovation and Agility: Faster innovation and accelerated change are key outcomes of industry clouds across all sectors, indicating that organizations should prioritize these benefits to remain competitive.
Conclusion

Cloud computing offers a myriad of benefits tailored to the unique needs of small businesses. By embracing cloud services, small enterprises can achieve significant cost savings, scalability, and flexibility, while enhancing collaboration and security. Furthermore, robust business continuity and disaster recovery solutions ensure operational resilience, and access to advanced technologies like AI and big data analytics fosters innovation and informed decision-making.
Industry Adoption Insights demonstrate that cloud computing is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different industries leverage cloud services to address specific challenges and capitalize on unique opportunities. Understanding these nuances helps small businesses in various sectors optimize their cloud strategies effectively.
As cloud technology continues to evolve, small businesses can leverage these advancements to stay competitive, adapt to market changes, and drive sustainable growth. By strategically adopting cloud computing, small businesses can transform their operations, unlock new opportunities, and thrive in an increasingly digital landscape.